Online 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping
Navigation
- Introduction
- What Is Rapid Prototyping?
- What Is the Rapid Prototyping Process?
- Are Rapid Prototyping Worth It?
- What Is 3D Printing?
- Are 3D Printing Worth It?
- Is Rapid Prototyping the Same as 3D Printing?
- What Is 3D Online Printing?
- Are 3D Online Printing Any Good?
- How Does 3D Online Printing Fulfill Rapid Prototyping Needs?
- How to Use 3D Online Printing Services for Your Rapid Prototyping Needs?
- How Much Does Online 3D Printing Cost?
- Who Is the Best 3D Online Printing Service Provider?
- Conclusion
Introduction
Rapid prototyping holds immense significance for companies and designers seeking to swiftly develop prototype models of novel products. By employing rapid prototyping methods such as 3D printing, prototypes can materialize within hours or days, as opposed to the lengthy weeks or months required by traditional prototyping techniques. For small businesses and independent designers, entrusting rapid prototyping services to online 3D printing providers entails notable advantages in terms of speed, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping refers to the utilization of technologies and techniques that expedite the creation of prototype models for physical products. It entails fabricating prototypes directly from digital data, such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files, without the need for extensive tooling and machining. The primary objective of rapid prototyping is to empower designers and engineers to swiftly assess and refine physical prototypes during the early stages of product development. Some of the prevailing rapid prototyping technologies employed today encompass:
- 3D Printing: Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing constructs objects layer by layer utilizing digital files. Prominent 3D printing technologies employed for rapid prototyping include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
- CNC Machining: Computer numerical control (CNC) machining swiftly carves prototypes from materials like metal, plastic, and wood using CAD files. While not as expeditious as 3D printing, CNC machining yields highly durable prototypes suitable for functional testing.
- Vacuum Casting: This method involves creating silicone molds from 3D printed parts, subsequently pouring liquid resins into the molds and allowing them to cure, resulting in urethane plastic prototype parts. Vacuum casting proves ideal for producing small batches of 10-100 prototype units.
What Is the Rapid Prototyping Process?
Here is an overview of the typical rapid prototyping process:
- Design Conceptualization
Develop initial ideas and concepts for the new product through sketching, CAD modeling, etc. Focus on key features and industrial design.
- Digital Prototyping
Create a digital 3D CAD model that defines the geometry, dimensions, and specifications needed for the physical prototype.
- File Preparation
Export and optimize the CAD file for 3D printing. Conduct model checks for printability and fix any issues.
- Select Process & Material
Determine the appropriate 3D printing technology and material based on prototype requirements, features, expected use, etc.
- Upload Design Files
Send 3D model files to the chosen manufacturing service bureau for quoting and production.
- Produce Prototype
The service bureau transfers files to the 3D printer and produces the prototype using the selected printing process and material.
- Apply Post-Processing
Additional steps like smoothing, coloring, coatings, etc. may be applied to improve prototype aesthetics and durability.
- Receive Prototype
The printed prototype model is shipped to the customer for inspection and testing.
- Evaluate & Refine
Review prototype against requirements, test functionality, and identify design changes needed.
- Iterate Design
Modify CAD model based on prototyping feedback. Repeat the process to produce improved design iterations.
The rapid iteration between digital and physical prototypes enabled by 3D printing accelerates the overall product development timeline.
Are Rapid Prototyping Worth It?
For most product development teams, especially those operating in competitive markets, the value delivered by integrating rapid prototyping into the design process is substantial and clear. The relatively small upfront investment in rapid prototyping technologies and services pays major dividends across key metrics like development costs, time-to-market, and product optimization.
By enabling hands-on testing of physical prototypes early in the design phase, rapid prototyping provides invaluable tangible feedback when changes are fastest and least expensive to implement. Rather than progressing for months using assumptions or virtual prototypes, developers can validate form, fit, and function against real-world conditions using rapid prototypes, saving tremendous time and money compared to reworking finished products.
Testing user interactions, ergonomics, part assemblies, manufacturability, and durability with physical prototypes also leads to far superior optimization of the design before major commitments are made to tooling and production. Flaws and areas for improvement are identified while rapid prototypes are still low-cost and design changes remain easy to implement. Finding issues after production would require expensive retooling and remanufacturing.
The combination of faster feedback and design optimization enabled by rapid prototyping ultimately leads to accelerated time-to-market. Getting viable prototypes in front of internal stakeholders, external partners, and end-users quickly builds momentum and enthusiasm for the new product. Rapid iteration then transforms this input into refined designs ready for production faster.
For companies navigating competitive business environments, rapid prototyping is becoming mandatory, not optional. The benefits in risk reduction, cost savings, speed, and innovation outweigh the minor investments in prototyping technology and services. Ultimately, rapid prototyping delivers major ROI both directly through lower costs and indirectly through higher-quality, better-optimized products that meet market demands.
What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a transformative technology for rapid prototyping and manufacturing applications. It works by joining materials together layer by layer based on a digital 3D model file, in contrast to subtractive methods like CNC machining that remove material from a solid block.
A 3D printer reads a CAD file containing the precise geometric design to be fabricated. Guided by this file, it deposits liquid or powder material in ultra-thin layers and fuses them together using techniques like extrusion, photopolymerization, or sintering. These layers accumulate on top of each other to construct the 3D object. Parts are built from the bottom up, layer by layer, until completion.
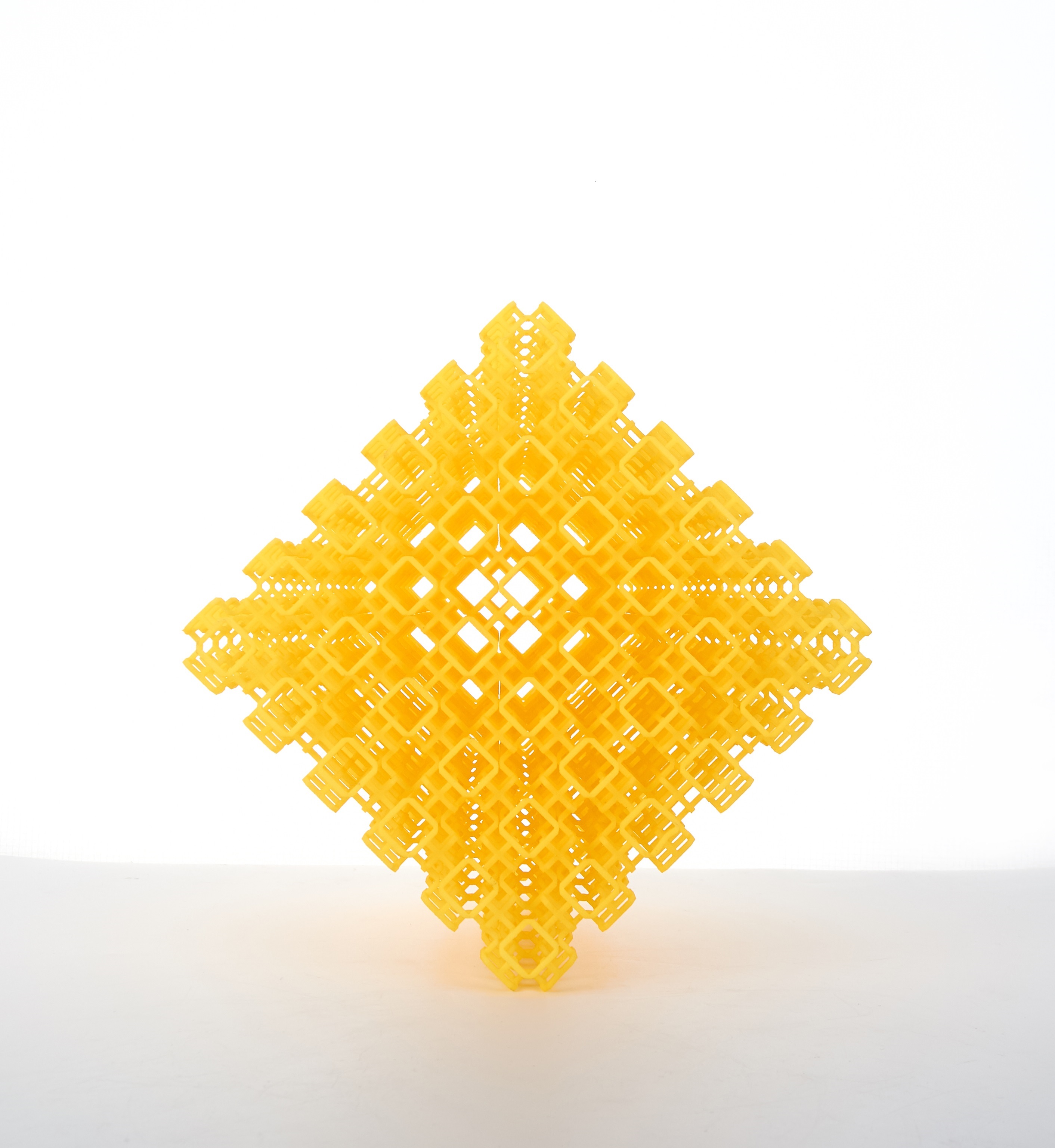
3D printing enables unprecedented freedom and efficiency in design and production compared to conventional manufacturing processes:
- Complex geometries such as delicate lattices, internal voids, and deep undercuts can be printed as easily as simple shapes. This enables completely new designs not possible through other methods.
- No tooling, jigs, or fixtures are required, eliminating costly and time-consuming setup while enabling rapid design iterations. The digital CAD file is the direct blueprint.
- Economies of scale are irrelevant. Parts can be profitably produced at any volume since no tooling investment is required. This enables distributed manufacturing.
- An expanding range of production-grade thermoplastics, composites, metals, and alloys can be printed, allowing the best material for each application.
- Desktop and benchtop 3D printers put prototyping and production capabilities on the user’s desk at affordable prices under $5,000.
These unique advantages have solidified 3D printing as an essential tool for rapid prototyping across many industries. It empowers designers to quickly translate digital concepts into physical forms for tactile analysis and functional testing. For transforming digital prototypes into tangible models, 3D printing delivers unprecedented agility and accessibility.
Are 3D Printing Worth It?
For both professional design teams and individual innovators, the value proposition of adopting 3D printing for rapid prototyping is compelling and clear. The technology delivers an ideal combination of speed, cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and physical prototype quality that empowers users to accelerate innovation initiatives.
Speed is a major advantage of 3D printing, with parts producible in hours and days rather than the weeks required for traditional model-making techniques. By eliminating CNC programming, cutting, tooling fabrication, and other lengthy preparatory work, 3D printing enables designers to obtain physical prototypes with minimal delay. This rapid iteration and feedback accelerates the overall development timeline.
Cost savings versus conventional prototyping methods are also substantial, with professional-grade desktop 3D printers available under $5,000 and basic models starting under $500. Online 3D printing services offer even greater value by eliminating equipment costs entirely, with high-quality prints available for as little as $10-$50 depending on size and material.
Ease-of-use is another benefit, as modern 3D printers and printing services offer very intuitive interfaces and workflow. Designers don’t need expertise in manufacturing or machining to go from CAD concept to prototype. The learning curve to integrate 3D printing is measured in hours or days rather than months of training.
Finally, print quality has improved tremendously in resolution, precision, surface finish, repeatability, and material options as 3D printing technology has matured. Parts exhibit the fidelity needed for reliable form, fit, and functionality tests.
With this rare combination of rapid turnaround, affordability, accessibility, and sufficient prototype quality, 3D printing delivers outstanding ROI as a tool to accelerate innovation. For most inventors and companies, investing in 3D printing either via desktop equipment or online services provides unmatched agility in translating ideas into physical reality.
Is Rapid Prototyping the Same as 3D Printing?
Rapid prototyping and 3D printing are not the same, for rapid prototyping is a broader concept that includes various techniques and methods to quickly fabricate a prototype while 3D printing is one of the many technologies under the umbrella of rapid prototyping.
What Is 3D Online Printing?
3D online printing pertains to internet-based services that empower users to procure 3D-printed components on a demand-driven basis, negating the requirement for personal 3D printing equipment. Users can effortlessly upload a digital 3D model, select from a myriad of printing materials, specify the quantity desired, and input both payment and shipping information. Once these steps are finalized, the online platform assumes the responsibility of producing the parts and delivering the completed prototypes straight to the user’s location.
For designers and emerging companies that lack in-house 3D printing capabilities, these online platforms present a quick and cost-effective alternative to harness the power of 3D printing, especially for rapid prototyping purposes. Several critical advantages of utilizing online 3D printing platforms are noteworthy:
- Equipment access: Get access to industrial-grade 3D printers without major upfront investment costs.
- Material options: Choose from an array of production-quality materials like thermoplastics, resins, metals, and specialty materials.
- Fast turnaround: Parts print rapidly after upload and ship within days of the order.
- Design freedom: Services accept all major 3D file formats and place no limits on geometry complexity.
- Low minimums: Single prints are possible, no volume orders required. Ideal for fast iterations.
- Cost savings: Pay only for what you need rather than unused printer capacity. Lower operation overhead.
For rapid prototyping needs, online services offer an extremely convenient and cost-efficient path to leveraging 3D printing, even for users with zero experience.
Are 3D Online Printing Any Good?
The online 3D printing industry has matured tremendously in recent years regarding print quality, materials, and reliability. For the vast majority of common rapid prototyping applications, today’s services meet or exceed expectations:
- Resolution: Layer resolutions down to 0.1mm are standard, enabling smooth surfaces on printed parts. Many services offer resolutions below 0.05mm for ultra-fine feature detail.
- Accuracy: Dimensional accuracy of printed parts now averages +/- 0.5mm or below, sufficient for most functional prototypes. Closer tolerances are achievable on professional-grade machines.
- Repeatability: Industrial printers deliver reliable consistency print-to-print for testing multiple iterations of the same design.
- Materials: Online printing services offer not just basic plastics like ABS but also advanced engineering resins, flexible materials, rubber-like elastomers, and metals. More exotic materials are also becoming available.
- Design freedom: No limits are placed on model geometry, enabling exploration of complex shapes and lattices impossible to produce through other methods.
- Quick delivery: Standard lead times are now 5-7 business days in the US, 14 days internationally. Rush build options can deliver in as little as 1-2 days.
For both visual prototypes to evaluate form and fit and functional prototypes requiring precise tolerances and durability, today’s online 3D print services offer impressive quality and consistency at very competitive prices. The breadth of materials and printing technologies now accessible online provides customizable solutions tailored to virtually any rapid prototyping application.
How Does 3D Online Printing Fulfill Rapid Prototyping Needs?
For design teams big and small alike, outsourcing 3D prints to online services has become the most convenient and cost-effective route for meeting nearly any rapid prototyping need:
- Faster iteration: Skip purchasing and maintaining printers by leveraging online services’ industrial capacity and rapid production and global shipment.
- Design verification: Test form, fit, ergonomics, and size with intricate printed models reflecting the exact planned design.
- Functional testing: Print durable prototypes from real engineering thermoplastics and metals to evaluate functionality for optimized performance.
- Customization: Many services offer custom finishing like dyeing, coatings, and textures for a complete representation of the planned final product.
- Presentation: Impress stakeholders, clients, and executives with accurate 3D printed renderings of the proposed product.
- Manufacturing analysis: Test prototype models for manufacturability and optimization for production processes.
- Short-run production: Use 3D printing services to economically produce small product runs to meet real user demand while prototyping.
For virtually any rapid prototyping need across the product development and testing process, today’s online 3D printing services offer the technology, quality, and capacity required to quickly turn digital designs into highly representative physical prototypes. Their breadth of materials, finishing options, speed, reliability, and economics ensure rapid prototyping with 3D printing services yields major ROI for innovators.
How to Use 3D Online Printing Services for Your Rapid Prototyping Needs?
Pre-Print Preparation
- Thoroughly check 3D model files for printability issues like gaps, non-manifold edges, unsuitable thicknesses, and stability. Repair models to avoid print failures.
- Consider the functional requirements and anticipated use to select the optimal material and printing process from those available.
- For critical dimensions, define tolerances clearly in notes when submitting orders rather than assuming default accuracy.
- Break larger models into smaller components to lower costs, speed production, and simplify post-processing.
Ordering
- Compare multiple online print services on cost, speed, and capabilities using instant quoting tools before ordering.
- Leverage lower resolution prints for early concept models, then iterate with higher resolution as the design progresses.
- Take advantage of online quotation calculators to explore different print materials, sizes, quantities, finishes, and delivery time combinations.
- For functional prototypes, opt for durable engineering thermoplastics or metals suited for the expected mechanical stresses during testing.
- Order spare copies of small intricate components that may be damaged during assembly or use.
Post-Processing
- To simulate production aesthetics, utilize available smoothing, coloring, coatings, textures, and other finishing processes.
- Light sanding and filling of voids can refine the surface finish. But take care not to damage the printed components.
- For assembly testing, insert separate fasteners into printed parts rather than trying to print the fasteners directly.
- Apply cyanoacrylate glue or epoxy to bond multi-part prints. Use alignment pins for precision mating interfaces.
- Leverage the service bureau’s expertise for finishing rather than attempting modifications in-house to avoid damaging prints.
Following these preparation, ordering, and post-processing best practices will enable online 3D printing to efficiently fulfill nearly any rapid prototyping need.
How Much Does Online 3D Printing Cost?
For very small parts under 2 cubic inches, prints can cost as little as $10-$25 in basic plastics. For reference, medium-sized prototyping parts range from $50-$150, while large or high-resolution prints are $200-$500+. With expedited builds and special materials or finishing, costs can reach thousands for very large or complex prototypes.
While online 3D printing reduces costs tremendously compared to in-house printing, users should leverage instant quoting tools extensively to right-size spending for each project phase. Services that offer applications engineering guidance are also beneficial to optimize costs.
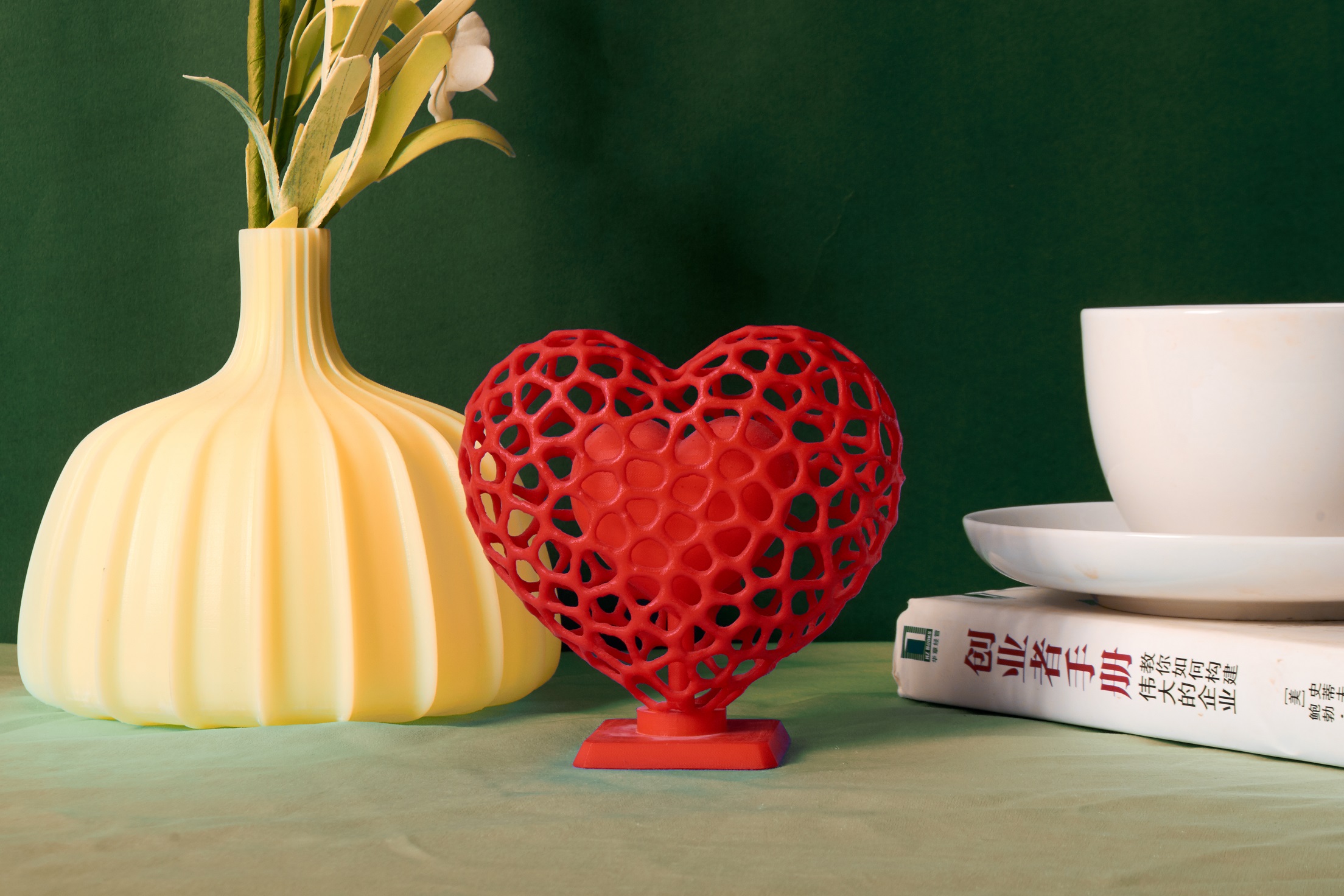

Who Is the Best 3D Online Printing Service Provider?
QSYrapid is the best 3D online printing service provider. With over 30 years of experience and 500 employees, QSYrapid provides fast, accurate quotes and convenient self-service ordering through its independently developed online system. The company has over 100 high-end 3D printers and post-processing equipment, enabling delivery in as fast as 24 hours. QSYrapid offers services includingautomated quoting, professional 3D printing with SLA, SLS, SLM, and other technologies, and surface finishing like polishing and painting.
With advanced 3D printing facilities, rigorous quality control, and certification to quality and information security standards, QSYrapid stands out as the best 3D online printing service provider. Key strengths include fast turnaround time, a wide range of printing technologies and materials, convenience of online ordering, competitive pricing with bulk order discounts, and professional customer service.
Conclusion
Companies and innovators can affordably incorporate rapid prototyping into their product development process at a very reasonable cost by utilizing online 3D printing services. The combination of industrial-grade printing capacity and materials, fast turnaround times, and application engineering expertise provided by the top service bureaus empowers users across industries to quickly iterate on physical prototypes of new designs with ease.
Outsourcing prints to an online 3D printing services provider like QSYrapid is a simple first step to unlocking faster design iteration at lower costs if rapid prototyping is a bottleneck in your current product development efforts. The ROI in terms of accelerating time to market, optimizing designs before tooling commitment, and establishing internal buy-in make online 3D printing services an indispensable partner for rapid prototyping success.