Your Top 5 3D Printing Questions — Answered
As 3D printing technology continues to advance and become more accessible, many people still have basic questions about how it all works and what its true capabilities are. This straightforward guide aims to address some of the most common curiosities surrounding 3D printing. We’ll explore the fundamental mechanics behind the different 3D printing methods, clarify what kinds of digital models and materials are compatible for 3D printing, highlight some key beneficiaries and innovative use cases across major industries, and provide examples of big companies utilizing this transformative technology.
How Does 3D Printing Actually Work?
While 3D printing seems like a complex, futuristic process, the core concept is actually quite simple. At its most basic level, it builds three-dimensional objects by gradually adding material layer-upon-layer.
Layer-by-Layer Construction
3D printing works by constructing objects one ultra-thin layer at a time using a computer-guided process. This additive approach is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing methods like machining that cut away from a solid block.
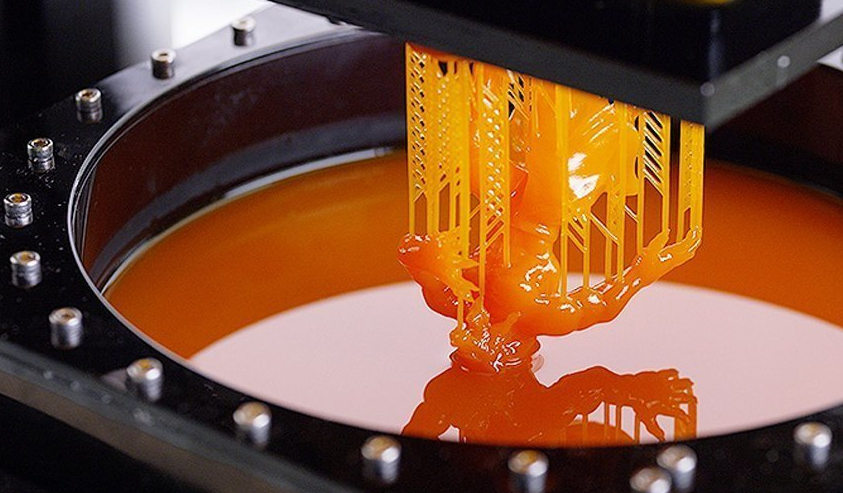
From Digital Model to Physical Object
Before printing, you need a 3D digital model of the object designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software or created from scan data. This digital blueprint tells the 3D printer exactly where to lay down or fuse each new layer of material.Read more: How to create a 3D prototype?
Different 3D Printing Technologies
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): One of the most popular and affordable 3D printing methods, FDM printers build objects by melting plastic filament and depositing it in precise layers via a heated nozzle.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use a laser to cure and solidify a liquid plastic resin layer-by-layer. This produces highly accurate, detailed prints.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS machines use a high-powered laser to fuse together small particles of plastic, metal, ceramic or glass powders, gradually building a solid 3D object one layer at a time.
While they build layer-upon-layer, each 3D printing technology differs in its specific method, compatible materials, cost, capabilities and ideal applications.For those interested in exploring the possibilities without investing in their own equipment, exploring the top-rated online 3D printing services can be a great starting point.

How Do I Know if My 3D Model Is Printable?
Before hitting print on a 3D model, there are some key factors to consider to ensure it can actually be properly 3D printed.
Structural Requirements
A structurally sound 3D model design is critical for successful printing. The model should:
- Have adequate wall thicknesses to be self-supporting
- Avoid extremely complex geometries that can’t be printed
- Incorporate features like escape holes if creating enclosed sections
Essentially, the 3D model needs to be a design that can be physically manufactured and hold its shape when printed.Learn more: 3D printing build volume optimization tips.
File Format and Resolution
In addition to the design itself, the way the 3D model file is formatted and prepared matters.
- It needs to be encoded in a compatible 3D file format like .STL, .OBJ or .AMF
- The resolution and number of triangles determines the printed surface quality
Complex models may need file repair, optimization, and refinement using specialized software before printing.Read more: 3D Printing STL File Related Content.
Model Checking Tools
There are various software tools and techniques that can analyze 3D models to identify any potential printability issues upfront, such as:
- Automated software that detects structural flaws or file errors
- Capability to slice models into print layers to preview issues
- Option to consult 3D printing experts for model validation
Taking steps to ensure your 3D model meets printability requirements prevents failed prints and produces a high-quality final part.
What Material Can You Use in a 3D Printer?
3D printers offer an incredibly diverse range of material options to suit any application’s requirements for properties like strength, flexibility, heat resistance and more.
Plastics
The most common 3D printing materials are plastic filaments, well-suited for prototyping and producing durable final products:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) – Made from renewable resources like corn starch, PLA is easy to print and has low warping issues, ideal for kids’ toys or low-stress parts.While generally considered safe, it’s wise to be mindful of any potential sensitivities and best practices when working with PLA, especially for projects intended for children.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) – With good impact resistance and heat deflection, ABS plastic is perfect for functional prototypes that require durability like automotive components.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) – Offering superior strength and temperature tolerance up to 230°F, food-safe PETG works well for food storage containers or kitchen tools.
Numerous specialty composites that blend plastics with materials like carbon fiber, metal or wood are also available for added reinforcement.
Metals
Metal 3D printing with technologies like direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) allows fabricating fully dense, functional parts from high-performance materials such as:
- Stainless Steel – Corrosion-resistant stainless makes great mold components, medical devices and industrial equipment.
- Titanium Alloys – Extremely strong and lightweight titanium is ideal for aerospace, automotive and orthopedic implants.
- Aluminum Alloys – Cost-effective aluminum is used for automotive components that require strength and thermal conductivity.
Advanced Materials
As 3D printing evolves, it continues expanding into new cutting-edge materials:
- Ceramics – Technical ceramic materials offer superior heat/chemical resistance ideal for high-temp manufacturing components.
- Sandstone – Sandstone printing produces realistic, full-color prototypes perfect for product visualization and marketing.
- Edibles – Food-safe ingredients let restaurants and bakeries 3D print intricate edible decorations and customized treats.
- Biomaterials – Biocompatible materials like polymers and living cells enable 3D bioprinting of artificial organs and human tissue.
From basic plastics to high-performance alloys and beyond, 3D printing’s material capabilities continue expanding to enable new engineering and product solutions.
Who Benefits Most From 3D Printing?
3D printing technology provides transformative advantages across many industries. Here are some of the biggest beneficiaries:
Healthcare Innovations
3D printing is revolutionizing healthcare in powerful ways:
- Prosthetics – Customized 3D printed prosthetic limbs can be tailored for an affordable, perfect fit.
- Bioprinting – 3D printers can combine living cells and biomaterials to create artificial organs and human tissue for transplants.
- Surgical Models – Printing highly accurate 3D models of a patient’s anatomy helps surgeons practice complex procedures.
Aerospace Advances
With 3D printing’s ability to produce lightweight yet super-strong parts, aerospace companies can:
- Prototype New Designs – Quickly iterate on new aircraft or rocket concepts during development phases.
- Produce Complex Geometries – Create intricate, one-piece fuel systems and engine components not possible with traditional manufacturing.
- Reduce Aircraft Weight – Optimize part designs to decrease weight while maintaining strength for improved fuel efficiency.
Customized Consumer Goods
3D printing enables mass customization and on-demand manufacturing of consumer products:
- Personalized Products – From custom hearing aids to insoles, eyewear to jewelry, products can be tailored precisely to each person.
- Creative Goods – Etsy sellers and artists leverage 3D printing to make unique, one-of-a-kind creative goods without expensive tooling.
- Home Decor – Affordable desktop printers let homeowners print replacement parts and customized decorations themselves.
While large-scale manufacturers harness 3D printing’s industrial capabilities, the technology is also empowering individual makers, small businesses, educators and hobbyists to innovate.
Which Companies Use 3D Printing Technology?
More and more major companies across industries are adopting and benefiting from 3D printing technology in innovative ways.
Aerospace and Automotive Leaders
Airbus, NASA, and SpaceX are among the aerospace leaders effectively employing 3D printing in their manufacturing processes. Airbus has incorporated over 1,000 3D printed parts in their A350 XWB aircraft, using high-performance materials that comply with industry regulations. NASA has utilized 3D printing to develop and test a space rover containing over 70 3D printed parts. SpaceX has used 3D printing to construct components for its Crew Dragon launch, such as the SuperDraco engine’s combustion chamber, which was fabricated using an advanced 3D printing technique and high-strength materials. 3D printing has allowed these companies to reduce costs, waste, and provide a more flexible production process while ensuring the necessary strength and durability of the components.
According to a Forbes article, 3D printing is transforming the automotive industry by optimizing inventory management and minimizing storage requirements. With the vast number of vehicles needing replacement parts, anticipating demand and storing the correct components can be difficult and costly. By utilizing 3D printing, automotive manufacturers can create parts on-demand, reducing the need for extensive storage facilities and related expenses. This flexible approach, as reported by Forbes, guarantees that the required parts are readily available, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction in the automotive aftermarket.
Medical Technology Innovations
3D printing is making significant strides in the medical field, as reported by the FDA. Some devices are mass-produced using a standard design, while others, known as patient-matched devices, are created using a patient’s imaging data. Examples include surgical guides, implants, and external prostheses. Researchers are also exploring the potential of 3D printing to create living organs, although this is still in the early stages. The FDA regulates 3D printed medical devices to ensure their safety and effectiveness, and patient-matched devices offer a more personalized approach to healthcare compared to conventionally manufactured devices with limited size options.
Small Business Solutions
Even smaller companies are taking advantage of 3D printing’s production flexibility:
- Custom Designs – Creating bespoke product designs for clients without expensive tooling changes.
- On-Demand Manufacturing – Print small batches or individual parts as needed to meet demand.
- Iterative Improvements – Rapidly update product versions by easily 3D printing changes.
From multinationals to startups, 3D printing enables faster innovation cycles, optimized designs, supply chain efficiencies, customization capabilities and production flexibility.
Explore 3D Printing’s Possibilities
3D printing technology goes far beyond creating basic plastic models. As covered in this guide, it enables manufacturing strong aerospace components, customized medical devices, innovative consumer products and more. With an ever-expanding range of printable materials from metals to biomaterials, 3D printing is redefining how products are designed and produced across industries. As the technology continues advancing in areas like precision and accessibility, the future applications are boundless. The time is now to utilize 3D printing’s transformative capabilities for your own projects and business needs.