Accelerating Product Development with QSYrapid’s Rapid Prototyping
Navigation
- Introduction
- what is Rapid Prototyping
- 3D Printing Prototype Technology: The Advantages It Offers
- Various 3D Printing Services
- Conclusion
Introduction
Question: What is rapid prototyping, also known as 3D printing?
Answer: Rapid prototyping, also referred to as 3D printing, signifies a groundbreaking approach to object formation. It metamorphoses digital schematics into tangible, three-dimensional entities. Using a layer-by-layer assembly, it fabricates sophisticated structures with remarkable speed and precision, thereby reinventing our traditional methods of material production.
what is Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping harnesses the potential of computer-aided design (CAD) software, interpreting digital blueprints of objects, deconstructing them into a series of two-dimensional cross-sections, and thereafter systematically reconstructing these layers. The result is a fully realized, intricate entity, much like the careful construction of a layered cake.
This technique signifies more than a simple conversion from digital to physical. It serves as a catalyst propelling manufacturing towards unprecedented efficiencies and cost reductions. The DNA of innovation is transformed; envision, for instance, a transition from concept to prototype within mere hours, rather than spanning weeks or even months.
Distinct from traditional scaling, where cost is linear with complexity, 3D printing erases this correlation. Fabrication of intricate geometries incurs no additional time or financial burden compared to simpler ones. This process significantly curtails costs, condenses developmental timelines, and minimizes waste when contrasted with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. As such, it is a significant contributor to both financial viability and ecological sustainability.
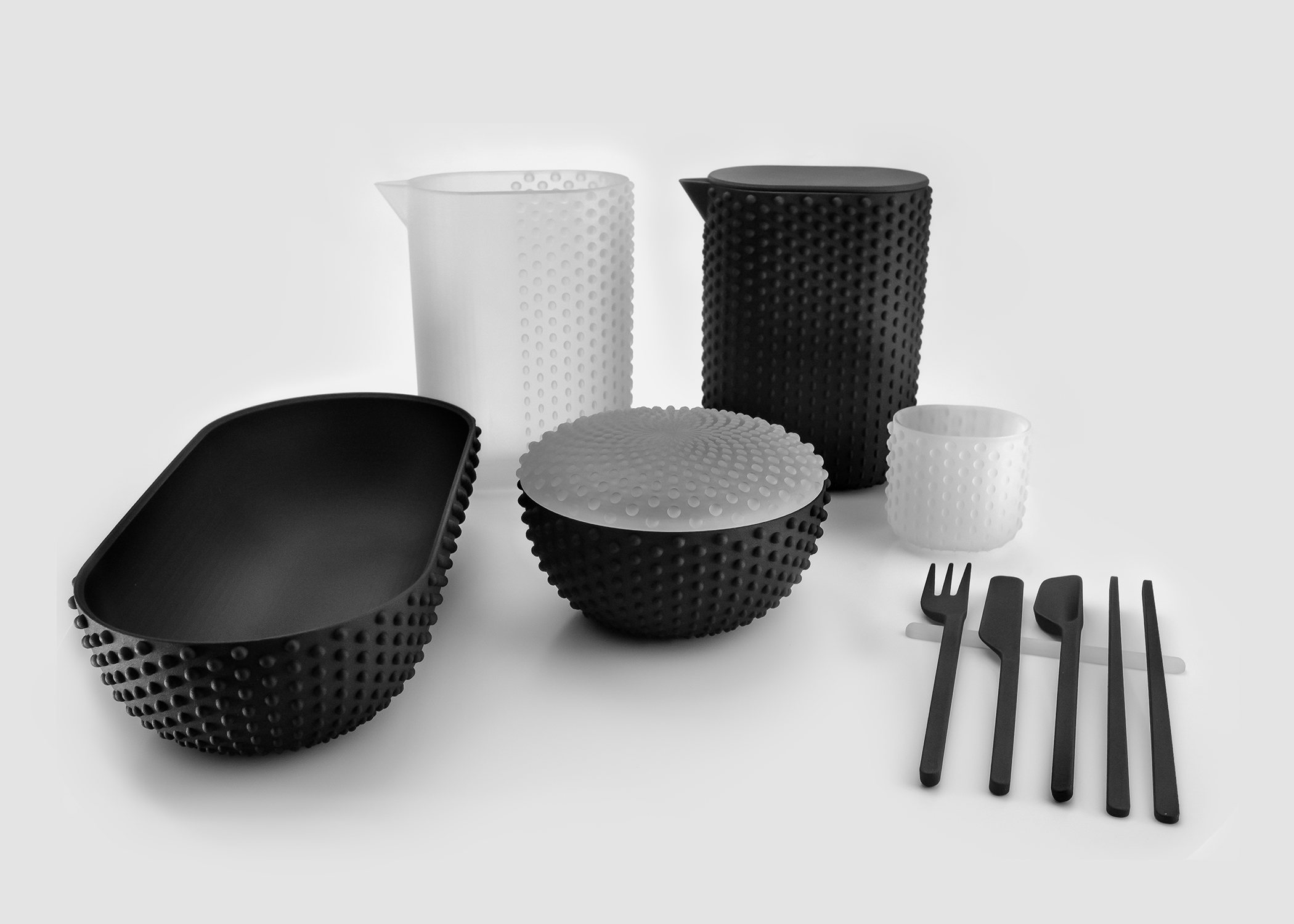

Rapid prototyping has thus inaugurated a multilateral evolution, recalibrating our design methodologies towards greater adaptability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. It functions as a conduit merging creativity with technology and realism with innovation, propelling the interplay between digital conceptualization and physical realization into previously uncharted terrain.
3D Printing Prototype Technology: The Advantages It Offers
Armed with a comprehensive understanding of rapid prototyping, let’s probe further into its transformative impact on the manufacturing sphere. The integration of 3D printing has precipitated a spate of benefits that overarch the realms of not just cost and time efficiency, but effect a comprehensive metamorphosis in our manufacturing modus operandi.
To elucidate the paradigmatic shift engendered by rapid prototyping, a comparison with traditional manufacturing techniques might prove insightful:
| Traditional Manufacturing | 3D Rapid Prototyping |
| Lengthy production time | Quick prototype creation |
| Higher costs for complex designs | Affordable, regardless of complexity |
| Material waste | Minimum waste |
| Limited design capabilities | Unlimited design possibilities |
| Requires multiple stages and tools | Single-step production |
In the updated comparison chart, the disparities between traditional manufacturing and rapid prototyping are articulated with greater clarity. Rapid prototyping shines through with qualities such as swift turnaround times, cost-efficiency in complex structures, minimal waste generation, unbound design liberties, and distillation of the production process into a singular step. It is indeed revolutionizing the manufacturing sector, quickening the rhythm of innovation, and shifting our perception concerning the process of object creation.
Various 3D Printing Services
As we delve deeper into the 3D printing terrain, we encounter a diversity of services, each with its unique characteristics and advantages, finely adapted to project-specific needs. Let’s examine three prominent types of 3D printing services, namely: SLA, SLS, and FDM.
Serving as the cornerstone for giving shape to concepts and refining designs, 3D Printing Prototypes offer rapid iterations prior to mass production. This fosters great flexibility in the nascent stages of a project.
- SLA (Stereolithography) 3D Printing Services excel in crafting highly detailed and smooth objects by harnessing a potent laser to solidify photoreactive resin, making it the preferred choice for projects mandating high accuracy or intricate detailing.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) 3D Printing Services utilizes a laser to fuse miniature polymer particles, resulting in robust, versatile objects. This method is particularly suited for functional prototypes and final-use components owing to its potential to produce sturdy items possessing commendable mechanical properties.
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) 3D Printing Services constructs objects by sequentially heating and extruding a thermoplastic filament. This cost-effective procedure is instrumental for creating prototypes, models, and production parts featuring simpler geometric designs.
Each of these services offers a unique set of advantages, implying that the most beneficial choice is contingent upon the specific needs and objectives of your project.
Conclusion
Throughout our journey into the world of rapid prototyping, we’ve dissected its unique rewards and become more acquainted with the variety of 3D printing services at our disposal. To encapsulate, rapid prototyping invigorates the tempo of innovation with swift, budget-friendly, and efficacious production that embodies boundless design scope.
In the realm of professional and trustworthy 3D printing services, QSYrapid leaves a notable impression with its expansive facility, brimming with the latest industrial machinery, and manned by seasoned engineers. With QSYrapid, you engage manufacturing expertise and the repository of knowledge to catapult your most pathbreaking ideas into reality.