What Is the Difference Between Industrial and Home 3D Printers?
3D printing has transformed how we create objects across industries and for personal use. Originally developed for prototyping, this technology now enables mass manufacturing and customized production. However, there are significant differences between the industrial-grade 3D printers used by businesses and the compact home 3D printers designed for hobbyists, educators, and makers. This article explores the key distinctions between these two printer types to help determine the right 3D printing solution based on specific needs and requirements. Understanding the capabilities, materials, costs, and complexities of industrial versus home 3D printers is essential for making an informed decision.
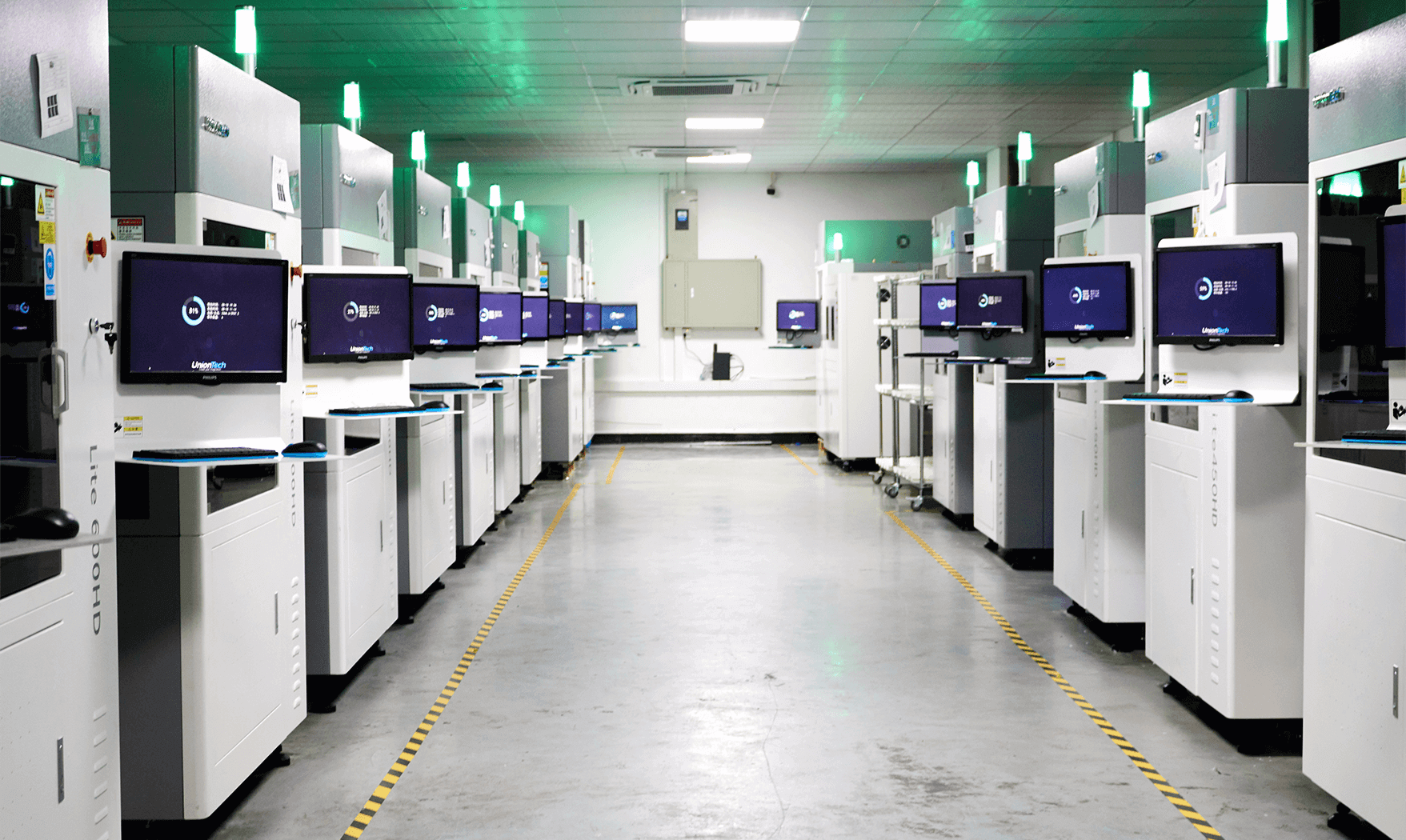
What Are Industrial 3D Printers?
For heavy-duty manufacturing tasks, industrial 3D printers are the solution. These robust systems cater to the exacting needs of professional applications.
1. Powering Large-Scale Production
Industrial 3D printers are advanced machines primarily employed for professional manufacturing, rapid prototyping, and large-scale production across multiple sectors. Their core function is to create high-precision, functional parts and components from a wide range of durable materials.
2. Industries Putting Industrial 3D Printers to Work
- Aerospace and Automotive Manufacturing: Industrial 3D printers are indispensable for producing complex, lightweight components for aircraft and vehicles with stringent quality and safety standards.
- Medical Device and Implant Fabrication: These printers enable the creation of customized medical devices, prosthetics, and implants tailored to individual patient needs using biocompatible materials.
- Construction and Architecture: In construction, industrial 3D printers can manufacture large structural elements, architectural features, and building components on-site.
3. Built for Industrial Reliability and Precision
- Massive Build Volumes: Industrial printers offer expansive build volumes, some large enough to 3D print full-scale components or architectural elements in one piece.
- High-Resolution and Advanced Materials: They achieve extremely precise resolutions and can print using specialized materials like metal alloys, engineering-grade plastics, and composites.
- Rugged and Continuous Operation: With robust, industrial-grade components, these printers are designed for heavy, reliable, and prolonged operation in demanding manufacturing environments.
Industrial 3D printers prioritize performance over simplicity. Their capabilities match the requirements of the most demanding industrial applications.

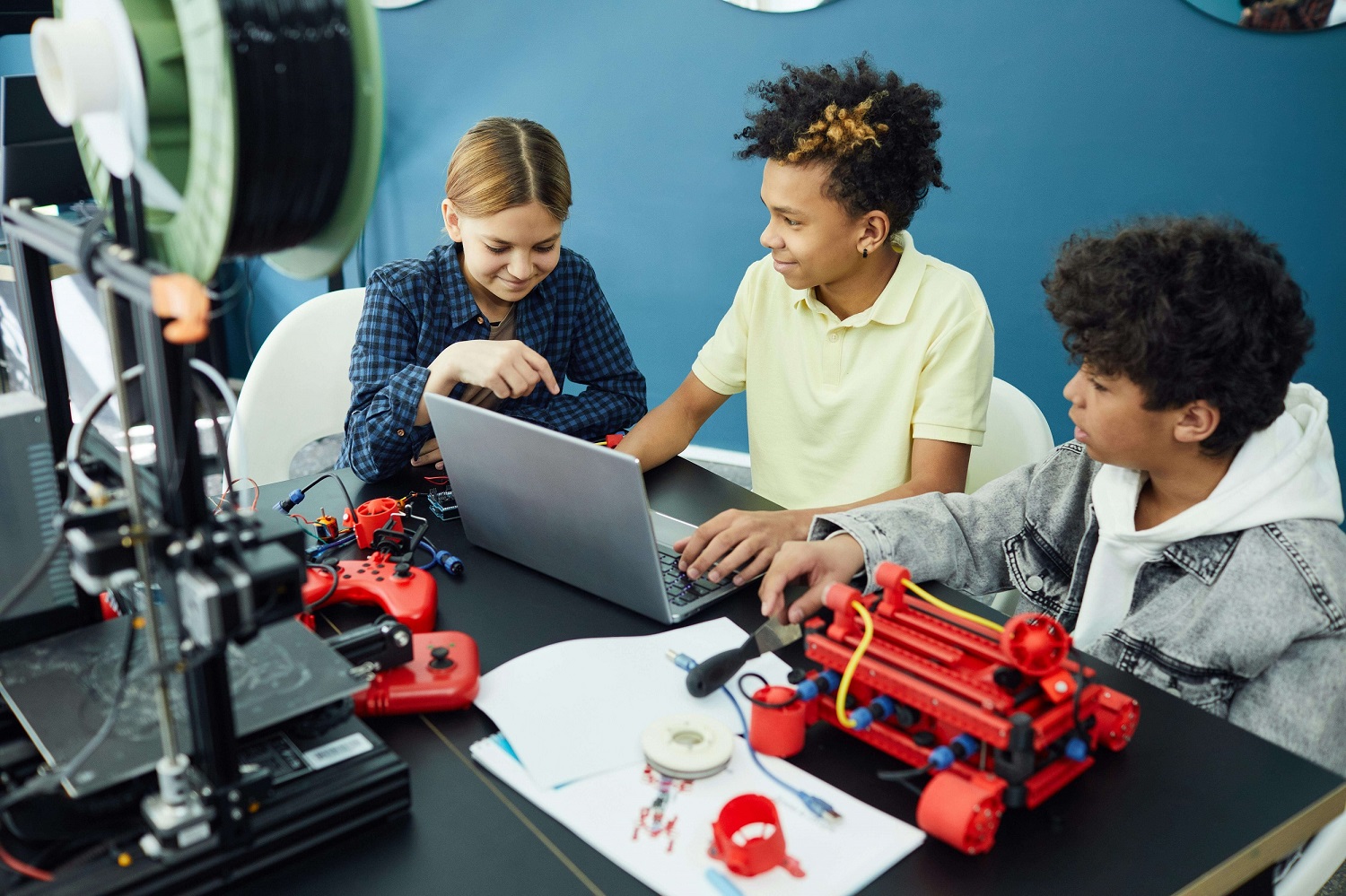
What Are Home 3D Printers?
For makers and creators at home, smaller desktop 3D printers are the go-to solution. These are designed for convenience and accessibility.
1. Personal 3D Printing for Creators and Hobbyists
Home 3D printers are compact desktop devices designed for individual use by hobbyists, makers, educators, and creative enthusiasts. Their main purpose is to provide an easy way to transform digital 3D designs into physical objects. Read more: How to use 3D printing for beginners.
2. Bringing Imaginative Ideas to Life
- Hobbyist Modeling and Prototyping: At home, users can 3D print their favorite characters, prototypes for inventions, or any 3D model they design.
- Hands-On Learning Tools: In classrooms, these printers allow students to visualize concepts by producing physical, 3D educational models and prototypes.
- Custom Art, Crafts, and Decor: For artistic projects, home 3D printers enable creating personalized home decor pieces, jewelry, figurines, and more.
3. Compact, User-Friendly Printing
- Space-Saving Desktop Design: With their small footprints, home 3D printers fit neatly on desktops or compact workspaces in homes, classrooms, or workshops.
- Easy Controls for Beginners: These plug-and-play devices feature simple, intuitive controls and interfaces tailored for new users of 3D printing.
- Common Desktop Filament Materials: While not as versatile as industrial printers, home units can still print using common desktop filaments like PLA, ABS, TPU, and PETG.
Home 3D printers put the power of additive manufacturing into the hands of makers, students, artists and hobbyists.

Industrial vs. Home 3D Printers: Key Differences Revealed
While both leverage 3D printing technology, there are significant distinctions between industrial-grade and home 3D printers. Let’s explore the major differences.
1. Build Volume Capabilities
Industrial Printers’ Massive Workspaces
Industrial 3D printers boast build volumes exponentially larger than desktop home units. Some can create components the size of an entire room. This accommodates printing full-scale prototypes, architectural elements, and oversized parts in one print.
Home Printers’ Compact Scales
In contrast, home 3D printers have relatively small build areas tailored for desktop use – usually up to around 300 x 300 x 300 mm. This size constraint limits home users to printing smaller objects and parts.
2. Print Quality and Materials
Industrial Precision and Advanced Materials
Industrial printers achieve extremely high resolution and layer precision, often down to 10-50 microns. They can also print using specialized materials like metal alloys, carbon fiber composites, and high-performance polymers.
Home User Materials and Tolerances
Most home units print in the 50-400 micron resolution range using common desktop filaments like PLA and ABS plastics. While decent quality, these lack the precision, strength, and diversity of industrial printer materials.
Click to learn the secrets of 3D printing resolution in detail.
3. Cost Factors
The investment levels for industrial and home printers show a stark contrast.
Industrial Investment Scales
Industrial 3D printers demand massive upfront investments from $20,000 to over $1 million. Operating costs for materials, facilities, and staffing further increase expenses for businesses. Learn more about the factors that affect the cost of 3D printers.
Consumer-Friendly Home Printer Costs
In the home market, 3D printers range from $200 to $3,000 – much more affordable for individuals. Material costs are also low, with common filament spools costing $20-50.
4. Speed and Production Rate
Industrial-Grade High Throughput
With rapid print speeds, large build volumes, and 24/7 operation capabilities, industrial printers can produce thousands of components quickly – ideal for mass manufacturing.
Moderate Home Print Speeds
Consumer-level home 3D printers produce parts much more slowly, better suited for custom one-off projects and small production batches by hobbyists.
These key differences highlight how industrial and home 3D printers serve vastly different scales of additive manufacturing needs.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printer for Various Needs
Selecting the ideal 3D printer requires carefully evaluating your specific goals and requirements. Whether for industrial manufacturing or home use, the right printer can unlock your innovation potential.
1. For Businesses Evaluating Industrial 3D Printers
When considering an industrial 3D printer for professional manufacturing operations, businesses should carefully assess their requirements and potential return on investment. Key factors to evaluate include:
- Production Volume and Part Sizes: Analyze production targets – the volume of parts needed and their dimensions. Ensure the printer’s build volume can accommodate your parts while enabling high throughput.
- Material and Precision Requirements: Determine if you need to print using specialized materials like metal, ceramic, or engineering-grade plastics. Also consider the part precision and resolution your applications demand.
- Integration with Existing Processes: Assess how well the industrial 3D printer integrates with your current manufacturing setup, software, and workflows to maximize efficiency.
- Overall Capital and Operating Costs: Industrial printers require significant capital investment, so evaluate the long-term total costs of ownership against projected returns and productivity gains.
2. For Hobbyists Seeking a Home 3D Printer
Making the transition to 3D printing at home starts with clearly understanding your needs and preferences as a user.
- Project Sizes and Build Area: Examine the typical sizes of objects and models you plan to print to ensure the build volume meets your needs without being excessively large.
- Material Needs and Print Quality: While home 3D printers primarily use plastics, some allow printing flexible, wood, or metallic composites. Determine your desired material capabilities and acceptable resolution.
- User-Friendliness and Support: As a beginner, prioritize printers with simple setup, intuitive controls, comprehensive documentation, and strong community support.
- Budgetary Constraints: Set a reasonable budget aligning with your needs, readiness to maintain the printer, and willingness to invest in this emerging technology.
3. Future-Proofing Your Investment
To truly future-proof your 3D printer investment, whether industrial or home, consider open material platforms that expand capabilities over time. Additionally, cloud-based printing solutions enable combining distributed 3D printers into unified production systems as your needs evolve.
The right 3D printer empowers you to turn ideas into reality efficiently and cost-effectively for your specific use case.
Bring Innovation to Life with 3D Printing
While vastly different in scale and capabilities, both industrial and desktop 3D printers harness transformative additive manufacturing technology. By carefully considering project needs, businesses and individuals can select the ideal 3D printer – whether producing high-volume components or creative models. As this technology continues advancing with new materials and cloud manufacturing, investing in adaptable systems ensures maximum long-term value. Regardless of the application, the right 3D printing solution empowers turning ideas into reality in innovative ways.